Report on the evaluation of the germicidal power of Cow Guard® nipple antiseptic

Cow Guard® nipple antiseptic was evaluated according to the cleaved teat method (Protocol A of the National Mastitis Council, USA, 1982), using the following methodology: (a) application of a suspension in milk of reference strains of Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 29740) and Escherichia coli (ATCC 35218) in known concentration, on cleaved cow teats (n=10 for each repetition); (b) disinfection of teats with the evaluated antiseptic with an exposure time of 10 minutes; (c) 10 nipples on which no antiseptic was applied were used as controls; (d) standardized rinsing with inactivating solution and counting of the number of colony forming units (CFU) of organisms recovered from teats treated with the antiseptic to be evaluated and the controls by bacterial culture. .
For rinsing the teats treated with Cow Guard®, as well as for the hydrogen peroxide-based positive control used in test 2, an inactivant based on lecithin, Tween 80 and sodium lauryl sulfate was used; while for rinsing the nipples treated with iodine-based antiseptic, 1% sodium thiosulfate was used. For S. aureus, salted mannitol agar (Britania) was used as test medium, while McConkey medium (Britania) was used for E. coli. A first brand commercial nipple antiseptic with a concentration of 10,000 ppm of available iodine and a commercial antiseptic based on hydrogen peroxide (0.5%) were used as positive controls. The CFU present on the plates were counted after a 24-h incubation period at 37°C. The count per nipple was obtained from the geometric mean of the plate counts, multiplied by the dilution factor and by 50 (total volume of liquid recovered). In cases where no organisms were recovered from treated teats, the value 0.01 was used instead of zero (0), since the geometric mean for zero is not defined.

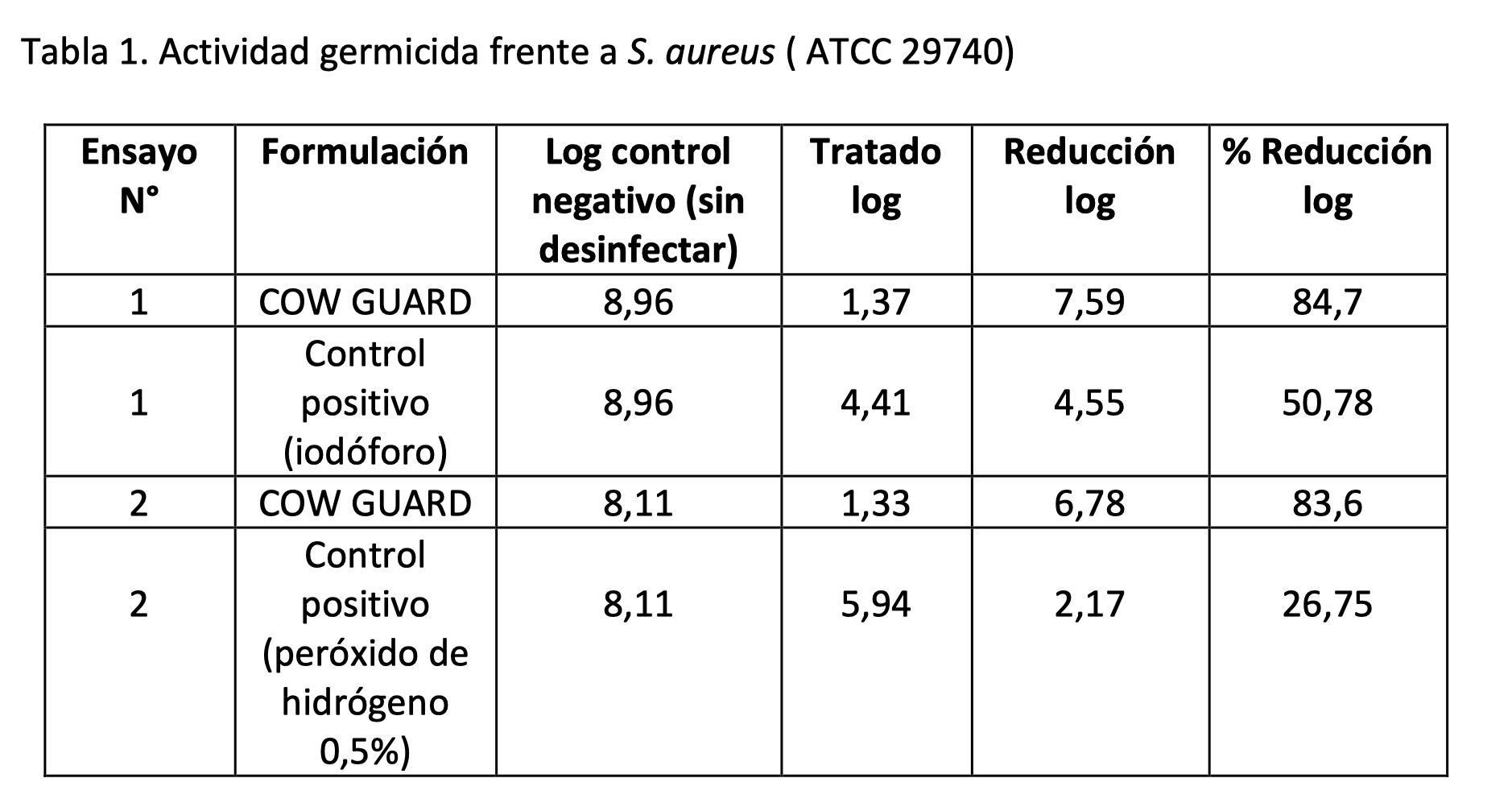
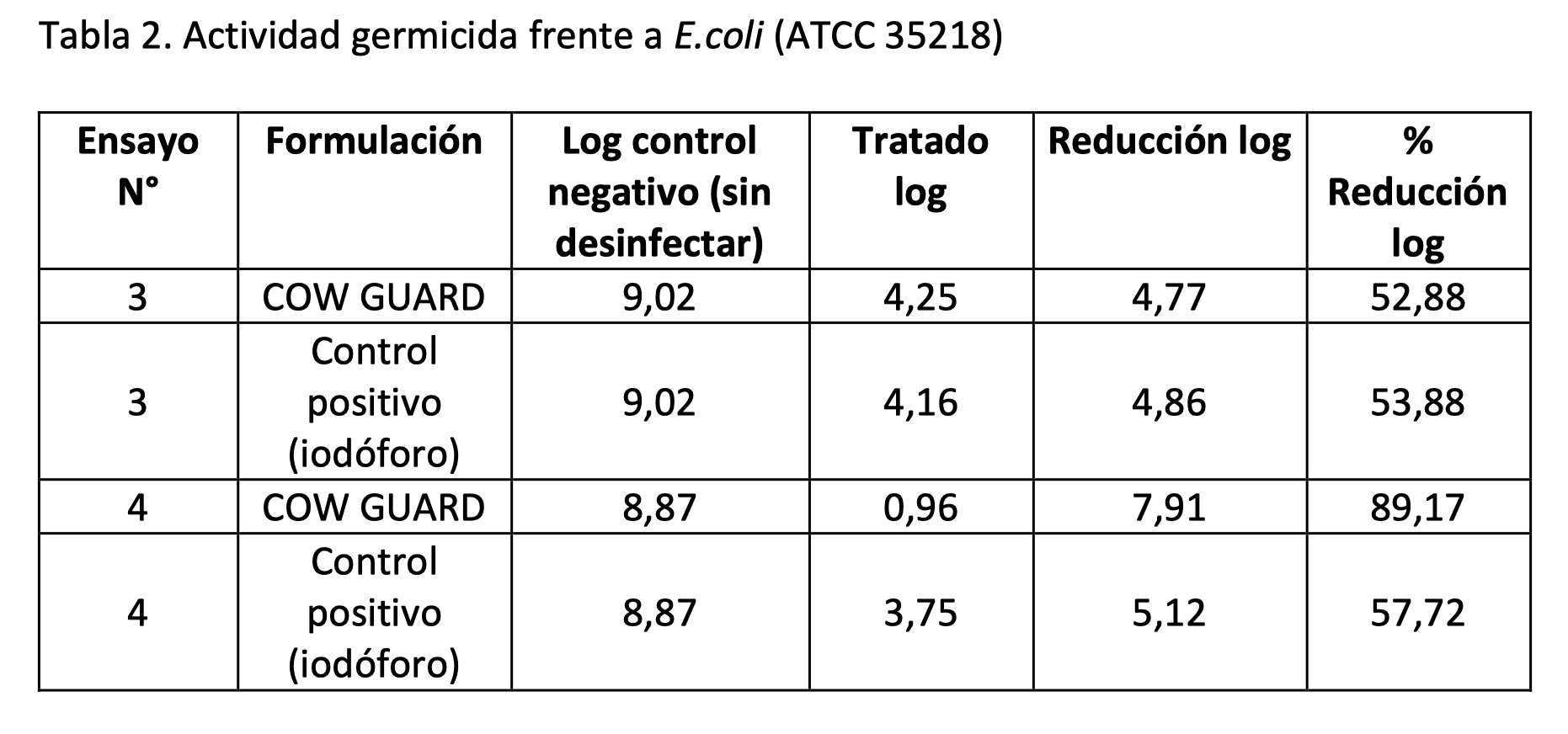
Tests against S. aureus were performed on (1) 10/08/16 and (2) 7/9/16; while against E. coli on (3) 1/11/16 and (4) 7/11/16. Below (Tables 1 and 2) are the results obtained expressed as log reduction and percentage of log reduction with respect to the control without disinfection.
Méd. Vet., PhD. MP 1774
